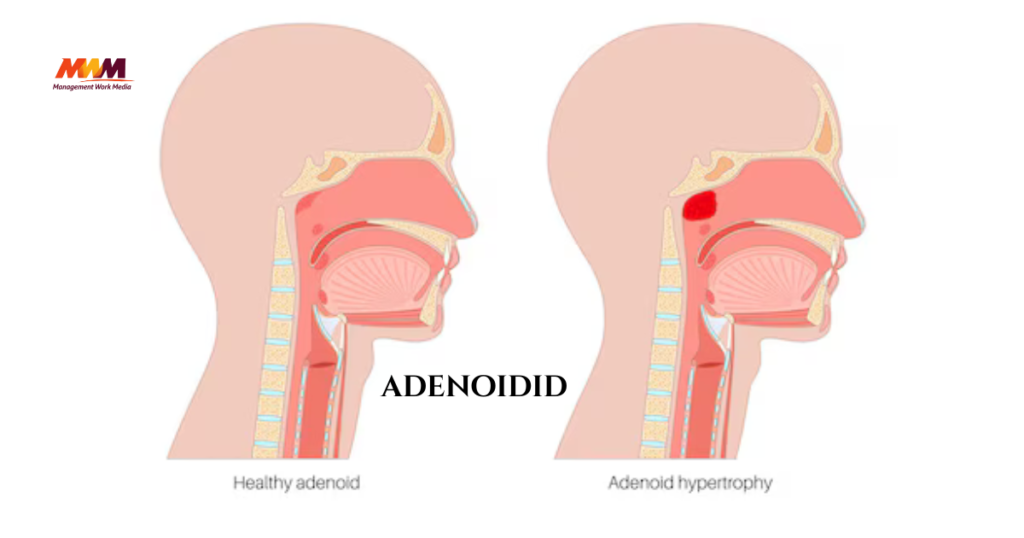
Adenoidid is an important but often overlooked part of a child’s health. These small lumps of tissue are located in the back of the nasal cavity and are part of the immune system. They help protect children from germs by acting as the first line of defense against viruses and bacteria. When adenoidid are healthy, they support childhood immunity and immune system development, helping children fight infections efficiently. However, when adenoidid become enlarged, they can cause problems like persistent nasal congestion, snoring in children, sleep apnea in kids, and ear infections due to Eustachian tube blockage.
Understanding adenoidid function is crucial for parents. These tissues work with the tonsils to trap pathogens entering the body through the nose and mouth. They help in antibody production, which builds immunological memory. This means the immune system can respond faster to future infections. Awareness of how adenoidid work and how they can become problematic allows parents to seek proper care and make informed decisions about pediatric ENT care and overall pediatric health.
Continue your journey with similar topics you’ll want to dive into.
What Are Adenoidid and Why They Matter
Adenoidid is a small but essential part of a child’s immune system. Located at the back of the nasal cavity, these tiny lumps of adenoid tissue help protect children from germs by acting as a first line of defense. While they play a crucial role in building childhood immunity, problems can occur when adenoidid become enlarged.
This enlargement can lead to nasal congestion, breathing difficulties, snoring in children, and frequent ear infections. Understanding adenoidid function, recognizing symptoms, and knowing the causes are essential for parents. This guide provides practical insights into adenoidid health, treatment options, and strategies to support children’s overall pediatric health.
How Adenoidid Function in Children’s Immunity
The adenoidid function is vital in building a child’s immune system. They act as a first line of defense, capturing bacteria and viruses before they can spread. By trapping pathogens in the nasal cavity, adenoidid reduce the risk of respiratory infections. They also play a key role in antibody production, helping the immune system learn to fight future infections efficiently.
These tissues are especially important for immune system development during early childhood. The adenoidid help the body develop immunological memory, which allows children to respond faster to common illnesses. While they naturally shrink as children grow, monitoring their function is crucial. Problems in adenoidid can interfere with childhood immunity and cause chronic issues like labored breathing or ear infections.
Signs and Symptoms of Enlarged Adenoidid
Symptoms of enlarged adenoidid are often easy to notice if parents pay attention. Children may have persistent nasal congestion, which looks like a constant cold. Snoring in children and sleep apnea in kids are common signs. Labored breathing at night can disrupt sleep and cause fatigue in children during the day.
Other signs include frequent ear infections due to Eustachian tube blockage. Children may develop speech impediments if airflow is restricted. Inflammation of throat and difficulty swallowing can also occur. Monitoring for these symptoms helps parents seek timely pediatric ENT care and prevent long-term complications.
Causes and Risk Factors for Adenoidid Problems
There are several risk factors for adenoidid enlargement. Frequent respiratory infections can cause adenoidid to swell. Allergic inflammation from conditions like asthma or hay fever may contribute to chronic enlargement. Environmental factors like secondhand smoke exposure and environmental pollutants also increase the risk.
Genetic predisposition can play a role, as children with family histories of adenoid problems are more likely to develop them. Lifestyle choices and immunity, such as diet, hydration, and outdoor activity, can also influence adenoidid health. Awareness of these causes helps parents plan preventative measures for adenoidid and reduce risks.
Diagnosis: How Doctors Identify Adenoidid Issues
Diagnosis of adenoidid usually begins with a thorough review of a child’s health history and symptoms. Pediatricians often look for persistent nasal congestion, labored breathing, and recurring ear infections. A physical examination may reveal swelling at the back of the throat.
Doctors may use endoscopic examination to get a clear view of the adenoidid. X-ray imaging for adenoids can also help determine the size of the enlargement. Accurate diagnosis is essential for deciding between mild vs severe adenoid enlargement and determining if surgery like adenoidectomy is necessary.
Explore more insights that go beyond the basics—click to uncover them.
Treatment Options: From Medications to Surgery
Treatment depends on the severity of the adenoidid problem. For mild vs severe adenoid enlargement, doctors may start with nasal steroids or antihistamines to reduce inflammation. These medications help relieve nasal congestion and improve breathing.
In cases where adenoidid cause sleep apnea in kids, chronic ear infections, or breathing difficulties, adenoidectomy may be recommended. Surgery removes the enlarged adenoidid and helps restore normal airflow. Recovery is usually quick, and most children experience significant improvement in sleep, breathing, and overall pediatric health after surgery.
Impact on Overall Health and Complications if Untreated
Untreated enlarged adenoidid can affect childhood immunity and overall health. Chronic nasal congestion and labored breathing can lead to sleep apnea in kids and fatigue in children. Ear infections from Eustachian tube blockage may cause hearing loss and recurrent pain.
Long-term complications include speech impediments, poor growth due to sleep disruption, and learning difficulties. Monitoring and early intervention prevent these issues. Parents who address frequent respiratory infections and allergic inflammation early help protect their child’s immune system development and overall well-being.
Coping Strategies and Support for Children
Children with enlarged adenoidid need both medical and emotional support. Coping strategies for children include creating a supportive environment at home and establishing calm bedtime routines. Gentle breathing exercises can reduce discomfort and improve sleep quality.
Parents should encourage fun activities that distract from labored breathing or discomfort. Engaging children in puzzles, reading, or playtime helps them feel better emotionally. Consulting with pediatric specialists and joining support groups provide additional reassurance and strengthen coping skills for children facing adenoidid issues.
Nutrition, Lifestyle, and Preventive Measures
Nutrition for adenoid health plays a major role in maintaining healthy tissues. A diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and proteins strengthens childhood immunity. Omega-3 fatty acids and inflammation control can reduce swelling and support overall health. Adequate hydration and mucous membranes maintenance help prevent nasal congestion and irritation.
Lifestyle choices and immunity matter. Regular outdoor activity, limiting secondhand smoke exposure, and controlling indoor environmental pollutants reduce the risk of adenoid problems. Preventative measures for adenoidid also include good hygiene, regular handwashing, and timely medical visits for early detection.
Regular Check-Ups and Integrating Pediatric Care
Routine check-ups are essential for monitoring adenoidid growth. Regular pediatric ENT care ensures early diagnosis of adenoidid issues. Pediatricians track frequent respiratory infections, nasal congestion, and sleep patterns to prevent complications.
Collaboration between parents and doctors helps maintain a child’s overall pediatric health. Monitoring recovery after adenoidectomy or medical treatment ensures long-term well-being. Early detection and continuous care help children develop normal breathing, strong immunity, and better sleep, which are critical for healthy growth and development.
FAQs
1. What is adenoidid, and why is it important in children?
Adenoidid are small lumps of adenoid tissue located at the back of the nasal cavity. They play a vital role in the immune system, acting as the first line of defense against germs. Healthy adenoidid help develop childhood immunity and protect children from respiratory infections.
2. What are the common symptoms of enlarged adenoidid?
Enlarged adenoidid can cause persistent nasal congestion, snoring in children, sleep apnea in kids, ear infections, labored breathing, and sometimes speech impediments. Parents may notice restless sleep or fatigue in children.
3. What causes adenoidid problems in children?
Frequent respiratory infections, allergic inflammation, environmental pollutants, and secondhand smoke exposure can enlarge adenoidid. Genetic predisposition also plays a role in some children.
4. How are adenoidid issues diagnosed?
Doctors may perform a physical exam, use endoscopic examination, or order X-ray imaging for adenoids. Accurate diagnosis of adenoidid helps determine whether mild vs severe adenoid enlargement is present.
5. What treatments are available for adenoidid problems?
Mild cases may use nasal steroids or antihistamines to reduce inflammation of throat. Severe cases may require adenoidectomy, a surgical removal of the enlarged adenoidid. Proper treatment improves breathing difficulties, sleep, and overall pediatric health.
Don’t miss our featured read—packed with insight you’ll want to know.